Lateral Lunges: How to Do It, Benefits, Muscles Worked, Mistakes
- Central Fitness
- Jul 15, 2025
- 20 min read
Updated: Dec 1, 2025
Lateral lunges are a cornerstone exercise for anyone looking to build stronger, more agile legs. This dynamic movement not only targets the major muscle groups in your legs, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, but also engages your core and stabilizer muscles, promoting balance and coordination.
As a versatile exercise, lateral lunges can be incorporated into various workout routines, ranging from strength training to mobility workouts. Their adaptability and effectiveness make them a favorite among athletes, fitness enthusiasts, and anyone aiming to enhance their lower body strength and agility.
The beauty of lateral lunges lies in their simplicity and the profound impact they have on leg strength and flexibility. Unlike traditional lunges that primarily focus on the front and back of the legs, lateral lunges emphasize the inner and outer thighs.
This is crucial for developing a well-rounded lower body strength, improving athletic performance, and reducing the risk of injury.
By incorporating lateral lunges into your workout regimen, you can achieve a more balanced and powerful leg musculature, essential for both everyday activities and competitive sports.
For those new to lateral lunges, the exercise might seem straightforward, but mastering the correct form is key to reaping the full benefits while minimizing the risk of injury. Proper execution ensures that the targeted muscles are effectively engaged and that the movement contributes to improved leg strength and stability.
As such, lateral lunges not only serve as a strength-building exercise but also as a tool for enhancing overall physical fitness and mobility.
Moreover, lateral lunges are highly adaptable, allowing for modifications to suit various fitness levels and goals.
Whether you're a beginner looking to improve your leg strength and balance or an advanced athlete seeking to enhance your agility and power, lateral lunges can be tailored to meet your specific needs.
This adaptability further extends to the inclusion of weights or resistance bands, making lateral lunges a versatile component of both bodyweight and weighted training programs.
In conclusion, lateral lunges are an invaluable exercise for anyone aiming to develop stronger, more agile legs. Their ability to target a wide range of muscle groups, combined with their adaptability and the benefits they offer for balance and coordination, makes them a must-have in any fitness routine.
Whether you're looking to improve your athletic performance or simply enhance your daily functional movements, incorporating lateral lunges into your workout regimen can lead to significant improvements in leg strength and overall physical health.
Table of Contents:
What is the Lateral Lunge Exercise
The Lateral Lunge is a dynamic, compound exercise that involves stepping directly to the side, shifting your weight onto the stepping leg while bending that knee, and keeping the opposite leg straight. This movement pattern challenges your body in the frontal plane - the side-to-side dimension of movement that's often neglected in traditional training programs.
Picture yourself standing tall with feet hip-width apart. You then take a controlled step directly to one side (let's say to the right), pushing your hips back and bending the knee of your stepping leg while keeping your left leg completely straight.
Your weight shifts over the stepping leg as you lower your body until your thigh is roughly parallel to the floor, creating a deep stretch in the inner thigh of your straight leg. From this position, you powerfully push off through the heel of your stepping foot to return to the starting position.
What makes the Lateral Lunge so incredibly valuable is its unique movement plane. While most exercises move you forward and backward (sagittal plane), the lateral lunge specifically targets the frontal plane, training muscles and movement patterns that are crucial for athletic performance but often overlooked in traditional gym routines.
The primary muscles targeted during lateral lunges include the adductors (inner thigh muscles) of the straight leg, which work eccentrically to control the descent and concentrically to help drive you back to center.
The gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and quadriceps of the stepping leg work powerfully to control the movement and drive you back to the starting position. Your core muscles engage intensely to maintain balance and prevent unwanted rotation.
Unilateral strength development is a key benefit of lateral lunges. By working one leg at a time, the exercise exposes and corrects strength imbalances between your left and right sides. This is crucial for athletic performance and injury prevention, as most sports and daily activities involve single-leg movements and changes of direction.
The hip mobility demands of lateral lunges are significant and beneficial. The exercise requires substantial flexibility in your adductors, hip flexors, and ankle joints. Regular practice can dramatically improve your hip mobility, which carries over to better performance in squats, deadlifts, and athletic movements.
Functional carryover is exceptional with lateral lunges. Think about stepping sideways to avoid an obstacle, getting in and out of a car, or making a defensive slide in basketball - all these movements rely on the same patterns trained in lateral lunges. This makes it one of the most practical exercises you can perform.
You can perform lateral lunges with just your bodyweight, making them incredibly accessible. For added resistance, you can hold CAP Barbell Rubber Hex Dumbbell Set or Rubber Hex Dumbbells in various positions - at your sides, in a goblet position against your chest, or even overhead for advanced practitioners.
The setup is straightforward but technique is crucial. Start with feet hip-width apart, chest up, and core engaged. Take a step that's wide enough to allow for a deep movement but not so wide that you lose control. Your stepping knee should track directly over your toes, and your straight leg should remain completely straight throughout the movement.
Progressive overload can be achieved through increased repetitions, added weight, slower tempos, or more challenging variations. The beauty of lateral lunges is that even small progressions can lead to significant improvements in strength, mobility, and athletic performance.
For those serious about maximizing their lateral movement training, proper nutrition becomes essential. Optimum Nutrition Gold Standard provides the high-quality protein necessary for muscle recovery and growth when combined with dynamic movement training.
To see the exercise performed with perfect technique and understand the movement mechanics, you can watch detailed demonstrations by searching "lateral lunge proper form" on YouTube.
Muscles Worked: Activating and Strengthening Key Leg Muscles

Lateral lunges are not just another leg exercise; they are a comprehensive movement that targets and activates key muscle groups in the legs, making them an essential component of any leg strengthening routine. This exercise is particularly beneficial for those looking to enhance their lower body strength, improve balance, and increase their range of motion.
The unique side-to-side movement of lateral lunges differentiates them from traditional lunges and squats, providing a multifaceted approach to leg training that addresses muscle groups often neglected in standard workouts.
The primary muscles worked during lateral lunges are the gluteus medius and gluteus minimus, located on the outer aspect of the buttocks. These muscles are crucial for hip stabilization, balance, and power.
By stepping to the side and bending the knee into a lunge, you're engaging these gluteal muscles in a way that they might not be used to, leading to improved strength and endurance in these key areas.
This is particularly beneficial for athletes who require lateral movement in their sport, but it's also advantageous for anyone looking to improve their functional fitness.
In addition to the gluteal muscles, lateral lunges extensively work the quadriceps. These four muscles at the front of the thigh are responsible for knee extension and play a significant role in walking, running, and jumping.
By performing lateral lunges, you're not only strengthening these muscles but also improving their coordination with other muscle groups, enhancing overall leg function and performance.
Another important muscle group targeted by lateral lunges is the adductors, or inner thigh muscles. These muscles are often overlooked in standard leg workouts, which can lead to imbalances and increased injury risk.
Lateral lunges require you to engage your adductors to stabilize your leg as you step to the side, providing a focused workout that strengthens these vital muscles and promotes better leg alignment and stability.
The hamstrings, located at the back of the thigh, also benefit from lateral lunges. Although they're not the primary focus of the movement, the hamstrings assist in hip extension and knee flexion during the exercise.
Strengthening the hamstrings in conjunction with the quadriceps and glutes can lead to more balanced leg muscle development and reduced injury risk, particularly in the knees.
Lateral lunges also engage the calf muscles, including the gastrocnemius and soleus. As you push back to the starting position, your calves work to extend the ankle and stabilize your leg.
Strong calf muscles are essential for explosive movements, running, and maintaining balance, making lateral lunges a valuable exercise for enhancing lower leg strength.
Beyond the muscle groups directly worked, lateral lunges also require a considerable amount of core engagement.
Maintaining balance and stability during the side-to-side movement challenges the abdominal and lower back muscles, contributing to a stronger, more stable core.
This core engagement is crucial for transferring power between the upper and lower body in both athletic endeavors and daily activities.
In summary, lateral lunges are a powerful exercise for activating and strengthening key leg muscles. By targeting the glutes, quadriceps, adductors, hamstrings, calves, and even the core, lateral lunges offer a comprehensive lower body workout that improves strength, balance, and functional mobility.
Whether you're an athlete looking to enhance your performance or simply seeking to improve your physical fitness, incorporating lateral lunges into your workout routine can lead to significant gains in leg strength and overall physical health.
How to do a Lateral Lunges

Lateral lunges are a dynamic exercise that targets multiple muscle groups in the lower body, making them an essential movement for anyone looking to enhance their leg strength, flexibility, and overall balance. This exercise is particularly beneficial because it mimics everyday movements, such as stepping aside to avoid an obstacle, thereby improving functional fitness.
To reap the full benefits of lateral lunges, it's crucial to perform them correctly. This guide will walk you through the steps to execute lateral lunges with proper form, ensuring you maximize their effectiveness while minimizing the risk of injury.
First and foremost, start by standing with your feet together, keeping your back straight and your shoulders back. This initial posture is important as it sets the foundation for a safe and effective lateral lunge.
Proper alignment from the very beginning helps in engaging the correct muscles and maintaining balance throughout the movement. This stance also prepares your body to move efficiently, making the exercise more effective.
To initiate the lateral lunge, take a large step to the side with one foot. This step should be wide enough to allow your body to lower into a lunge without your knee extending past your toes.
This is crucial for protecting your knee joints and ensuring that the focus remains on strengthening the leg muscles. The wider step also increases the engagement of the gluteal muscles, which are key targets of lateral lunges.
As you step out to the side, begin to bend the knee of the leg you stepped out with, pushing your hips back as if you're sitting into a chair. It's important to keep the other leg straight, with the foot firmly planted on the ground. This not only helps in balancing but also stretches the inner thigh muscles of the straight leg, enhancing the flexibility benefits of lateral lunges.
Ensure that your chest remains lifted and your core engaged throughout the movement. This engagement is crucial for maintaining balance and stability, which are key components of correctly performing lateral lunges. A strong, engaged core prevents you from leaning too far forward or backward, allowing for a more effective workout and reducing the risk of lower back strain.
Once you've lowered your body into the lunge, with the thigh of the bent leg parallel to the ground, press through the heel of the bent leg to return to the starting position.
This part of the movement activates the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, providing a comprehensive leg workout.
The action of pushing back to the starting position also challenges your balance and core stability further, enhancing the exercise's benefits.
It's essential to perform lateral lunges on both sides to ensure balanced muscle development and flexibility.
Alternating sides also helps in maintaining an even level of strength and agility, which is crucial for both athletic performance and daily activities. Consistency in performing lateral lunges on both sides promotes symmetrical muscle growth and prevents potential muscle imbalances.
In conclusion, lateral lunges are a versatile and effective exercise for strengthening and toning the legs, improving balance, and increasing flexibility. By following these detailed steps, you can ensure that you're performing lateral lunges with proper form, maximizing their benefits while minimizing the risk of injury.
Whether you're an athlete looking to enhance your performance or someone aiming to improve their physical fitness, incorporating lateral lunges into your workout routine can lead to significant improvements in your lower body strength and overall health.
Benefits of the Lateral Lunge Exercise
The benefits of incorporating Lateral Lunges into your training routine extend far beyond just building stronger legs. This exercise creates a cascade of positive adaptations that will transform how you move, perform, and protect yourself from injury.
Enhanced Athletic Performance
Agility and change of direction improvements are immediate and dramatic with consistent lateral lunge training. Sports like basketball, soccer, tennis, football, and hockey all demand rapid lateral movements and quick direction changes. By training in the frontal plane, you build the explosive power and control needed to accelerate, decelerate, and change direction with lightning speed and precision.
Lateral power development is crucial for athletic success but often overlooked in traditional training. The ability to push off sideways, shuffle defensively, or make explosive cuts separates good athletes from great ones. Lateral lunges directly target these movement patterns, building the kind of power that translates immediately to improved sports performance.
Balance and coordination are significantly enhanced through lateral lunge training. The unilateral nature of the exercise, combined with the side-to-side movement, forces your body to stabilize in challenging positions. This improves your proprioception (body awareness) and overall movement control, making you more graceful and efficient in all activities.
To support explosive athletic performance, Creatine or Optimum Nutrition Creatine Monohydrate Plus Powder can enhance your power output and help maintain intensity during challenging lateral movement sessions.
Injury Prevention Powerhouse
Knee stability improvements are one of the most valuable benefits of lateral lunges. Many knee injuries, including ACL tears and patellofemoral pain, occur during lateral movements or when the knee collapses inward (valgus collapse).
By strengthening the adductors, abductors, and hip stabilizers, lateral lunges help keep your knees tracking properly and reduce dangerous forces that can lead to injury.
Hip health and stability benefit tremendously from lateral lunge training. The exercise strengthens the muscles that support your hip joint from all angles, improving overall stability and reducing the risk of common hip issues. The deep range of motion also enhances hip mobility, which can alleviate tightness and improve movement quality.
Ankle strength and stability are challenged and improved as you control the lateral movement and push off to return to center. This helps fortify your ankles against sprains and improves your ability to react to uneven surfaces or unexpected movements.
Functional Strength and Mobility
Real-world movement enhancement is where lateral lunges truly shine. Consider the movements you make daily: stepping out of the way of an obstacle, reaching for something on a shelf, getting in and out of vehicles, or navigating crowded spaces. All these activities involve lateral movement patterns that are directly trained through lateral lunges.
Improved hip mobility is a key benefit that carries over to all your other exercises. The deep stretch in the adductors and the demand on hip rotation help increase your range of motion significantly. This improved mobility can enhance your performance in squats, deadlifts, and virtually every lower body exercise.
Balanced muscle development is achieved by targeting the often-neglected inner and outer thigh muscles. Most people have strong muscles in the sagittal plane (front and back) but weak muscles in the frontal plane (side to side). Lateral lunges address this imbalance, creating more symmetrical and resilient lower body strength.
Aesthetic and Physique Benefits
Inner thigh toning and strengthening is a major benefit for those focused on physique development. The adductors are heavily targeted during lateral lunges, helping to tone and strengthen this often-problematic area. The exercise also improves the shape and definition of your entire leg.
Glute development is enhanced, particularly the gluteus medius and minimus, which are crucial for hip stability and the coveted "side glute" development that creates an impressive physique from all angles.
Accessibility and Versatility
Equipment-free training makes lateral lunges perfect for home workouts, travel, or when gym access is limited. You can perform them anywhere with just enough space to step sideways. A yoga mat or Amazon Basics 1/2 Inch Extra Thick Exercise Yoga Mat can provide a stable, comfortable surface for practice.
Scalability allows the exercise to challenge everyone from beginners to elite athletes. Start with bodyweight and progress to holding Bowflex SelectTech Adjustable Dumbbells or adjustable dumbbells for added resistance.
Low learning curve makes lateral lunges accessible to people of all fitness levels. The movement pattern is intuitive and can be learned quickly, making it an excellent exercise for beginners while still being challenging enough for advanced practitioners.
For enhanced recovery and muscle development from lateral training, ensure adequate protein intake with whey protein and consider Optimum Nutrition Serious Mass Weight Gainer if you're looking to build overall mass.
To see these benefits demonstrated by athletes and fitness professionals, explore comprehensive analyses by searching "lateral lunge benefits" on YouTube.
Variations of the Lateral Lunge Exercise
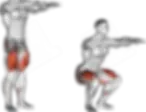
The Lateral Lunge offers incredible versatility through numerous variations that can accommodate different fitness levels, equipment availability, and specific training goals. Each variation provides unique challenges and benefits for comprehensive lower body development.
Bodyweight Lateral Lunge
The Bodyweight Lateral Lunge is the perfect starting point for mastering the movement pattern and building foundational strength and mobility. Focus on controlled movement, pushing your hips back, and maintaining proper knee alignment. This variation is excellent for warm-ups, rehabilitation, or when you want to add volume without external load.
Practice on a yoga mat or Amazon Basics 1/2 Inch Extra Thick Exercise Yoga Mat for better grip and comfort during the movement.
Dumbbell Lateral Lunge Variations
Dumbbells at Sides: Hold a CAP Barbell Rubber Hex Dumbbell Set or Rubber Hex Dumbbells in each hand, letting them hang naturally at your sides. This allows for heavier loading and focuses primarily on leg strength while challenging your grip and core stability.
Goblet Lateral Lunge: Hold a single dumbbell vertically against your chest, cupping one end with both hands. This front-loaded position encourages a more upright torso and increases core engagement. Bowflex SelectTech Adjustable Dumbbells or adjustable dumbbells are excellent for this variation as you can easily adjust the weight.
Single-Arm Lateral Lunge: Hold a single dumbbell in one hand, either at your side or in the goblet position. This creates an asymmetrical load that significantly increases the demand on your core stabilizers and anti-rotation muscles.
Resistance Band Lateral Lunge
Using Resistance Bands adds a unique challenge to lateral lunges. You can:
Loop a band around your ankles: This provides resistance as you step out and forces your abductors to work harder
Loop a band above your knees: This helps activate your glutes and teaches proper knee tracking
Hold band handles: Anchor the band and hold handles for upper body involvement
The accommodating resistance of bands provides increasing tension as you step out, creating a unique stimulus that can enhance the exercise's effectiveness.
Kettlebell Lateral Lunge
Using kettlebells or an Iron Kettlebell for Dumbbell provides a different grip and weight distribution compared to dumbbells. You can hold the kettlebell:
Goblet style: Similar to dumbbell goblet lunges but with the unique kettlebell grip
Bottoms-up: Hold the kettlebell upside down for an extreme stability challenge
Racked position: Hold the kettlebell at shoulder height for increased core demands
Advanced Lateral Lunge Variations
Lateral Lunge with Reach: As you lunge to the side, reach your opposite hand toward your stepping foot or even to the floor. This increases the range of motion and engages your core and obliques more intensely while adding a rotational component.
Lateral Lunge to Curtsy Lunge Combo: Combine a lateral lunge with a curtsy lunge (stepping diagonally behind the other leg). This creates a fluid, multi-planar movement that targets the glutes and inner/outer thighs from different angles.
Jumping Lateral Lunge: Add an explosive component by jumping laterally from side to side, landing in a lateral lunge position. This plyometric variation builds explosive power and agility.
Lateral Lunge with Overhead Press: Hold dumbbells and perform an overhead press as you return to the standing position. This creates a full-body exercise that challenges coordination and stability.
Tempo and Range of Motion Variations
Slow Eccentric Lateral Lunge: Emphasize the lowering phase by taking 3-5 seconds to descend into the lunge. This increases time under tension and can enhance both strength and flexibility gains.
Pause Lateral Lunge: Hold the bottom position for 2-3 seconds before returning to standing. This eliminates the stretch reflex and requires greater strength to initiate the return movement.
Deficit Lateral Lunge: Stand on a platform or step to increase the range of motion for the straight leg. This creates a deeper stretch and greater challenge but should only be attempted with excellent mobility and form.
Unilateral Progressions
Single-Leg Lateral Lunge: Instead of returning to a bilateral stance, step directly from one lateral lunge into another on the same side. This creates continuous unilateral loading and significantly increases the stability challenge.
Lateral Lunge to Single-Leg Stand: After completing the lateral lunge, lift the non-working leg off the ground and hold a single-leg stand for 2-3 seconds before the next repetition.
Programming Different Variations
Beginners should master bodyweight lateral lunges before progressing to weighted variations. Intermediate lifters can incorporate dumbbell and resistance band variations for increased challenge. Advanced athletes can use jumping variations, complex combinations, and deficit versions for maximum difficulty.
To support your training across all variations, Pre-Workout Supplements can provide the energy and focus needed for challenging lateral movement sessions, while Creatine Monohydrate Powder MuscleTech Cell-Tech can enhance power output and recovery.
For comprehensive demonstrations of all these variations, explore detailed tutorials by searching "lateral lunge variations" on YouTube.
Frequently Asked Questions About This Exercise
Lateral Lunges often generate questions regarding their execution, benefits, and how they fit into a comprehensive training program due to their unique movement pattern and frontal plane emphasis.
How Deep Should I Go in a Lateral Lunge?
Aim to descend until the thigh of your stepping leg is roughly parallel to the floor, or as deep as your mobility allows while maintaining proper form. Your straight leg should remain completely straight, and your chest should stay upright throughout the movement.
Never sacrifice form for depth. If you can't maintain proper knee alignment over your toes, or if you experience pain, reduce the depth and work on improving your mobility over time. Foam Rollers and Stretching Straps can help improve hip and ankle mobility for deeper, safer lunges.
What Are Common Mistakes to Avoid During Lateral Lunges?
Knee valgus (knee caving inward) is the most critical mistake and can be dangerous. Ensure your stepping knee tracks directly over your toes throughout the entire movement. Focus on pushing your knee outward and engaging your glutes.
Leaning too far forward shifts the load away from your legs and onto your lower back. Keep your chest up and push your hips back to maintain proper posture. Not pushing hips back reduces glute and hamstring activation - initiate the movement with a hip hinge.
Straight leg bending defeats the purpose of the exercise. The non-stepping leg should remain completely straight to maximize the stretch on the adductors and maintain proper movement mechanics.
How Often Should I Do Lateral Lunges?
Frequency depends on your overall training program and recovery capacity. For most individuals, incorporating lateral lunges 1-2 times per week as part of a lower body workout is sufficient. If you're focusing heavily on frontal plane strength or agility training, you might perform them more often.
The relatively lighter loading and unique movement pattern often allow for higher frequency compared to heavy bilateral exercises, but always ensure adequate recovery between sessions.
Can Lateral Lunges Help with Knee Pain?
In many cases, yes! Lateral lunges strengthen the muscles that stabilize the knee joint, particularly the gluteus medius and adductors. By improving hip stability and proper knee tracking, they can help alleviate certain types of knee pain, such as patellofemoral pain syndrome.
However, if you have pre-existing knee pain, consult a healthcare professional or physical therapist before incorporating this exercise. Start with bodyweight and focus on perfect form if cleared to perform the movement.
Do Lateral Lunges Work Your Glutes?
Yes, significantly! While they heavily target the adductors, your gluteus maximus and gluteus medius on the stepping leg are crucial for hip extension and stabilization. The gluteus medius, in particular, works hard to prevent your hip from dropping and maintain proper pelvic alignment.
The stepping leg's glutes work powerfully to drive you back to the center position, making lateral lunges excellent for overall glute development.
What's the Difference Between a Lateral Lunge and a Side Lunge?
The terms "lateral lunge" and "side lunge" are often used interchangeably to describe the same exercise: stepping directly to the side and bending one knee while keeping the other leg straight. There is no widely recognized technical difference between the two terms.
Can I Do Lateral Lunges at Home Without Equipment?
Absolutely! Bodyweight lateral lunges are highly effective and require no equipment, making them perfect for home workouts. You can increase the challenge by increasing repetitions, slowing the tempo, adding pauses, or progressing to single-leg variations.
A yoga mat can provide better grip and comfort, especially on smooth floors.
How Long Does It Take to See Results from Lateral Lunges?
Strength and stability improvements can typically be noticed within 2-3 weeks of consistent training. Functional improvements (better agility, reduced knee discomfort) often appear within 4-6 weeks, while visible muscle development usually takes 6-8 weeks of proper training combined with adequate nutrition and recovery.
To support muscle growth and recovery from lateral training, ensure adequate protein intake with Optimum Nutrition Gold Standard and consider Optimum Nutrition Serious Mass Weight Gainer if you're looking to build overall mass.
Are Lateral Lunges Good for Runners?
Yes, very beneficial! Runners primarily move in the sagittal plane (forward and backward), but strong frontal plane muscles are crucial for stability, injury prevention, and efficient force transfer. Lateral lunges strengthen the hip abductors and adductors, which help stabilize the pelvis and knees during running.
This can reduce the risk of common running injuries like IT band syndrome, runner's knee, and hip pain while improving overall running efficiency and form.
Should I Feel Lateral Lunges in My Inner Thighs?
Yes, you should feel a significant stretch and activation in your inner thighs (adductors), particularly in the straight leg. This is one of the primary benefits of the exercise. You should also feel your glutes and quadriceps working in the stepping leg.
If you don't feel the stretch in your adductors, try taking a wider step or focusing on keeping your straight leg completely straight throughout the movement.
Can Lateral Lunges Replace Regular Lunges?
While lateral lunges are incredibly valuable, they complement rather than replace traditional forward or reverse lunges. Each variation targets different movement patterns and muscle emphases. For complete lower body development, incorporate both sagittal plane (forward/backward) and frontal plane (lateral) movements.
For enhanced training performance and recovery, consider Creatine for improved power output and Pre-Workout Supplements for enhanced focus and energy during challenging lateral movement sessions.
Conclusion About Lateral Lunges

Following our exploration of lateral lunges and their alternatives, it's clear that this exercise holds a significant place in any comprehensive lower body workout regimen.
Lateral lunges, with their unique side-to-side movement, target and strengthen a variety of muscle groups in a way that few other exercises can match.
This conclusion aims to encapsulate the multifaceted benefits of lateral lunges, reinforcing why they should be a staple in your fitness routine.
Lateral lunges excel in enhancing lower body strength, particularly in the glutes, quadriceps, and adductor muscle groups. This strength is crucial not only for athletic performance but also for daily activities, improving overall functionality and reducing the risk of injury.
The emphasis on these specific muscles helps in creating a balanced and powerful lower body, which is essential for stability and movement efficiency.
Moreover, lateral lunges contribute significantly to improving balance and coordination. The lateral movement requires a level of control and stability that engages the core and lower body in a harmonious effort to maintain posture and alignment.
This coordination between muscle groups is beneficial for athletic pursuits and everyday tasks alike, making lateral lunges a practical exercise for enhancing physical balance.
Flexibility and range of motion see noticeable improvements with regular practice of lateral lunges. By stepping out to the side and lowering into a lunge, you're stretching the inner thigh muscles of the straight leg, as well as the hip flexors and glutes of the bent leg.
This dynamic stretch not only aids in muscle recovery but also promotes a greater range of motion, which is vital for injury prevention and overall mobility.
Incorporating lateral lunges into your workout routine also offers the advantage of versatility. Whether you're a beginner or an advanced athlete, lateral lunges can be adjusted in intensity to match your fitness level.
dditionally, they can be performed anywhere, requiring no special equipment, making them an accessible exercise for everyone looking to improve their lower body strength and flexibility.
The cardiovascular benefits of lateral lunges should not be overlooked. Although primarily a strength-training exercise, performing lateral lunges at a faster pace or incorporating them into a high-intensity interval training (HIIT) workout can increase heart rate and boost cardiovascular health.
This dual benefit of strengthening and cardiovascular conditioning makes lateral lunges a highly efficient workout choice.
It's also worth noting the psychological benefits of mastering a challenging exercise like lateral lunges. Achieving proficiency in this movement can boost confidence and motivation, encouraging a positive attitude towards fitness and physical health. The sense of accomplishment from improving in lateral lunges can inspire you to tackle other challenging exercises, fostering a growth mindset.
In conclusion, lateral lunges are a powerhouse of an exercise, offering a wide array of benefits for strength, balance, flexibility, and cardiovascular health. Their versatility and adaptability make them suitable for a broad spectrum of fitness enthusiasts, from beginners to seasoned athletes.
By integrating lateral lunges into your workout routine, you're not just enhancing your lower body strength; you're investing in a more balanced, flexible, and capable physique. As we've seen through exploration and comparison with alternative exercises, lateral lunges stand out as a key movement for anyone serious about their fitness and overall well-being.
See More Exercises: ⤵
.webp)